Can a Portable Power Station Replace a Generator?
The rising need for reliable and eco-friendly power solutions makes it important to understand the various options available. Portable power stations and traditional generators are often at the forefront of this discussion. Each comes with unique attributes suited to different needs, but can a portable power station truly replace a generator?
This blog will delve into the basic concepts and functionalities of portable power stations and generators. We will explore their key differences, highlight the unique benefits that portable power stations offer over generators, and discuss scenarios to determine the best choice for your specific needs. By the end, you’ll have a clearer understanding of which option is more suitable based on your energy requirements and environmental considerations.
Understanding the Basics: Portable Power Stations vs. Generators
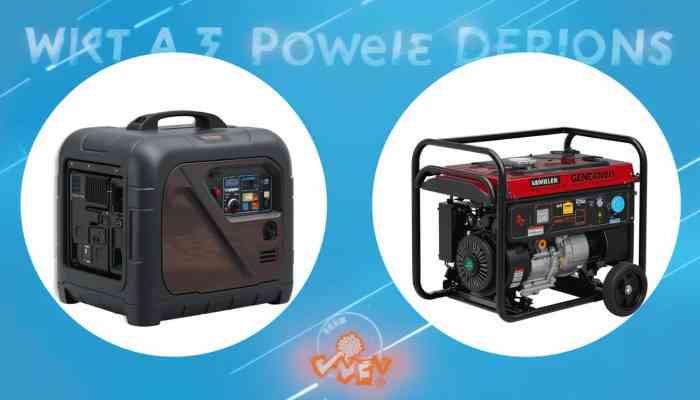
What is a Portable Power Station?
A portable power station is a compact, rechargeable battery-powered unit designed for carrying and providing electricity in a variety of settings. Typically equipped with multiple output ports such as AC, DC, and USB, these devices can charge electronics, power small appliances, and serve as a backup power source in case of emergencies. They often incorporate lithium-ion or lithium-polymer batteries and can be charged using standard AC outlets, car sockets, and increasingly, solar panels, making them versatile and convenient.
Unlike traditional generators, portable power stations operate silently and emit no fumes, making them suitable for indoor and outdoor use without any health hazards. They are gaining popularity owing to their eco-friendly nature, ease of use, and the convenience they offer in quickly setting up a reliable power supply wherever needed.
What is a Generator?
Generators are machines designed to convert various forms of energy into electrical power. The most common types use gasoline, diesel, or natural gas to drive an internal combustion engine, which in turn drives an alternator to produce electricity. Generators are capable of delivering considerable power output, making them suitable for running high-wattage appliances and machinery, thereby serving as primary power sources for homes, outdoor activities, and industrial sites.
However, generators come with notable drawbacks. They emit exhaust fumes, produce significant noise, and require regular maintenance to ensure optimal functionality. These issues can limit their practicality in terms of indoor use and environmental friendliness. Despite these limitations, their ability to deliver high-capacity power for prolonged durations makes them indispensable in scenarios where consistent and robust power is critical.
Key Differences Between Portable Power Stations and Generators
Power Output and Capacity
The primary distinction between portable power stations and generators lies in their power output and capacity. Portable power stations usually offer lower wattage and are ideal for powering small to medium electronics like smartphones, laptops, lights, and small appliances. Their battery capacity is measured in watt-hours (Wh) and generally ranges from 100Wh to several thousand watt-hours, catering to portable and short-term energy needs.
In contrast, generators, powered by internal combustion engines, can deliver significantly higher wattage, often ranging from 500 watts to several thousand watts. This capacity is suitable for energy-intensive appliances such as refrigerators, air conditioners, power tools, and larger equipment. Generators are thus more suited for heavy-duty applications and extended power outages, where substantial and sustained power is mandatory.
Noise, Emissions, and Environmental Impact
One of the major selling points of portable power stations is their quiet operation. They generate electricity silently, as they lack moving parts like those in traditional generators. This attribute makes them perfect for noise-sensitive environments like campsites, homes, and public spaces.
Generators, on the other hand, are known for their loud operation due to the internal combustion engine. The noise levels can be disruptive, especially in residential areas. Moreover, the engines emit exhaust gases that contain harmful pollutants, raising environmental and health concerns. Regular maintenance, including fuel refills and oil changes, adds to the environmental footprint of generators.
In comparison, portable power stations produce zero emissions and run on clean energy sources. This makes them a more eco-friendly option, aligning with the growing global emphasis on sustainability and reducing carbon footprints.
Benefits of Portable Power Stations Over Generators
Portability and Convenience
Portable power stations score high on portability and user convenience. Designed to be compact and lightweight, they can easily be transported, set up, and operated without requiring technical expertise. Their simple plug-and-play functionality means you can quickly provide power to your devices without the need for fuel or extensive preparation.
On the other hand, generators, while portable to an extent, are generally heavier and bulkier due to their engines and fuel tanks. Moving them around often requires substantial effort, and setting them up involves checking fuel levels, starting the engine, and managing exhaust emissions, which can be cumbersome, especially in remote or quick-deployment scenarios.
Clean Energy and Eco-Friendly Operation
The shift towards clean energy has amplified the appeal of portable power stations. These devices use rechargeable batteries, which can be renewed via grid power or solar panels, making their operation practically emission-free. This feature is crucial for eco-conscious users and adherence to increasingly stringent environmental regulations.
Generators, by contrast, consume fossil fuels and emit carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and other pollutants. This not only affects air quality but also poses health risks, particularly in enclosed or populated areas. Even though some generators are designed to be somewhat cleaner and quieter, they still can’t match the environmental friendliness of portable power stations.
When Should You Use a Portable Power Station or a Generator?
Best Use Cases for Portable Power Stations
Portable power stations are ideal for scenarios requiring moderate power levels and where noise and emissions are a concern. They are perfect for camping trips, outdoor events, and emergency preparedness kits. Backpackers, outdoor enthusiasts, and homeowners looking for a quiet, non-intrusive power source will find them highly beneficial. Their ease of use and the capacity to be charged by solar panels make them great for off-grid living and other eco-friendly applications.
When to Choose a Generator Instead
Generators remain the go-to solution for powering heavy-duty machines and appliances over extended periods. They are irreplaceable in situations like prolonged power outages, construction sites, and events where consistent and substantial power is crucial. Generators provide the muscle needed to keep large electronic systems operational and can run for extended hours as long as fuel is available. If high power output and the ability to run large equipment are required, generators still hold the upper hand.
Conclusion
Deciding between a portable power station and a generator hinges on your specific power needs, environmental considerations, and the importance you place on portability and convenience. Portable power stations offer a clean, quiet, and user-friendly option for moderate power requirements, particularly in eco-sensitive or noise-restricted scenarios. They stand out for their ease of use and environmental benefits.
Generators, despite their drawbacks, are irreplaceable for their high power output and robustness in handling demanding and long-term power needs. The choice ultimately comes down to assessing your needs, and the operating environment, and balancing the importance of convenience against power capacity. By understanding the strengths of each, you can make an informed choice that aligns with your energy needs and sustainability goals.