Thyroid Cancer Treatment in Singapore: Making Informed Decisions
People with thyroid cancer must know all of their options, particularly those looking for treatment in Singapore. A trustworthy local resource for information about thyroid nodules and thyroid cancer treatment options in Singapore highlights the importance of delivering treatment based on a thorough understanding. In most cases, identifying the best course of treatment for thyroid cancer is the first step in dealing with the disease. Combination therapies, including surgery, hormone therapy, radioactive iodine, targeted medicines, and active monitoring, are available for low-risk situations.
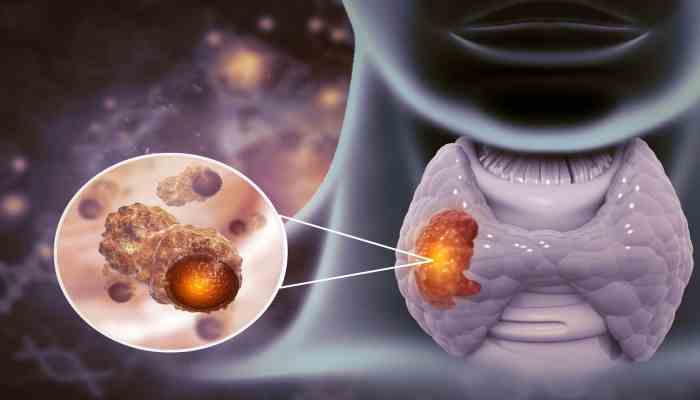
What is Thyroid Cancer
Cancer of the thyroid begins with thyroid cells, a butterfly-shaped organ in the neck that makes chemicals that control your metabolism, turning cancerous and growing into a tumor. In its early stages, it usually doesn’t cause any signs. However, as it worsens, you may experience a lump in your neck, changes in your voice, such as hoarseness, or difficulty swallowing. The good news is that most kinds of thyroid cancer can be cured, mainly if they are found early. There are a lot of different ways to treat this condition, ranging from active surveillance for simple, low-risk cases to surgery, radioactive iodine therapy, and other more advanced choices for more complicated cases.
Latest Treatments Available in Singapore
Active Surveillance: Ideal for small, low-risk papillary thyroid cancers confined within the gland.
- Involves periodic ultrasounds and blood tests.
- Helps avoid overtreatment in cases that are unlikely to progress.
Surgical Options
- Lobectomy (partial thyroidectomy): Removal of one thyroid lobe. Used for small or unifocal tumors.
- Total thyroidectomy: Removing the entire gland; typical for larger or bilateral tumors.
- Neck lymph node dissection: Performed if cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes.
Robotic/Endoscopic Surgery
- Less invasive techniques, such as transaxillary and behind-the-ear approaches, are used to reduce visible scarring.
Radioactive Iodine (RAI) Treatment
- Used after surgery to eliminate remaining thyroid tissue or microscopic cancer cells.
- Taken orally in capsule or liquid form, RAI specifically targets thyroid cells.
External Beam Radiotherapy (EBRT)
- Administered over several weeks through daily sessions.
- Reserved for cancers resistant to surgery/RAI or those that have spread locally or to bones.
Thyroid Hormone Replacement & Suppression Therapy
- Patients take daily levothyroxine after surgery to replace natural hormone production.
- Also used to suppress TSH, a hormone that can fuel thyroid cancer growth.
Targeted Therapies & Immunotherapy
- Utilized in advanced, metastatic, or RAI-refractory thyroid cancers.
- Targeted drugs, such as tyrosine kinase inhibitors (e.g., sorafenib, lenvatinib, selpercatinib, pralsetinib), address specific genetic changes in cancer cells.
- Immunotherapies are emerging but remain primarily in the clinical trial stage.
Alcohol Ablation (Ethanol Injection)
- A procedure that is performed with little invasiveness and is used to cure tiny residual cancer in lymph nodes, especially when surgery isn’t suitable.
Comparing Different Treatment Options
Here is a list of thyroid cancer treatments, how invasive they are, what they can be used for, and how long they take to heal and keep an eye on:
Active Surveillance
- How Invasive: None.
- Great for: Small (less than 1 cm) and low-risk papillary cancers.
- Recovery & Monitoring: Involves regular tests with no physical recovery time.
Lobectomy
- How Invasive: Moderate.
- Great For: Small, localized tumors.
- Recovery & Monitoring: Recovery typically takes a few weeks; lifelong hormone treatment may not be necessary.
Total Thyroidectomy
- How Invasive: Major.
- Great For: Larger or multifocal tumors, higher-risk cancers.
- Recovery & Monitoring: 1–2 months to heal; lifelong hormone treatment is needed.
Radioactive Iodine (RAI) Therapy
- How Invasive: None.
- Great for: After surgery to clear residual tissue.
- Recovery & Monitoring: Short isolation period; months of monitoring
External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT)
- How Invasive: Moderate-high.
- Great for: Non-RAI responsive or extensive spread.
- Recovery & Monitoring: Months of daily sessions; longer side effects.
Immune/Targeted Therapy
- How Invasive: Systemic.
- Great For: Advanced or metastatic cancer.
- Recovery & Monitoring: Varies; lifelong monitoring is recommended.
Alcohol Ablation
- How Invasive: Low.
- Great For: Small recurrences in lymph nodes.
- Recovery & Monitoring: A relatively straightforward operation that calls for additional scans.
Factors Affecting Cost
The cost of a treatment for thyroid cancer in Singapore depends on several things, such as
- Treatment Complexity: More involved treatments, such as complex surgeries or combination therapies, naturally incur higher costs
- Hospital Choice: Private hospitals are generally more expensive than public ones.
- Medical Fees: Highly experienced surgeons and specialists may charge more.
- Technology Used: Advanced techniques, such as robotic surgery or specialized diagnostic tests, increase overall costs.
- Hospital Stay & Isolation: The duration of your hospital stay, including any isolation periods for treatments like RAI, affects the total expense.
- Long-Term Medications: Lifelong thyroid hormone replacement therapy involves ongoing costs.
- Follow-up care, including regular monitoring of scans and blood testing, drives up the total cost.
- Insurance Coverage: MediShield Life, MediSave, and private Integrated Shield Plans reduce out-of-pocket payments. Confirming coverage with your provider is essential.
Understanding these elements will help you accurately estimate the costs of thyroid cancer treatment in Singapore.
Who Is a Suitable Candidate for Each Treatment?
Understanding which treatment is most suitable for different patient profiles is vital:
- Active Surveillance: Best for small, non-spreading papillary cancers, or for elderly/high-risk patients who prefer watchful waiting.
- Lobectomy: For a single, small (under 4 cm) low-risk tumor in one lobe, aiming to preserve part of the thyroid.
- Total Thyroidectomy: For larger tumors, multifocal disease, lymph node spread, aggressive cancers, or when the lowest recurrence risk is desired.
- Radioactive Iodine (RAI) Therapy: Used after thyroidectomy to eliminate remaining normal tissue and microscopic cancer cells, especially with lymph node or distant spread.
- External Beam Radiotherapy (EBRT): For cases not responding to RAI, local recurrences unsuitable for surgery, or to control metastases in critical areas.
- Immunotherapy & Targeted Therapy: For advanced, widespread, or RAI-resistant cancers, particularly those with specific genetic mutations.
- Alcohol Ablation: For small, localized recurrences in lymph nodes, especially when further surgery isn’t an option.
When you know what to look for, you can choose the most effective treatment path based on the patient’s overall condition and the cancer’s unique characteristics.
Do’s & Don’ts When Preparing
Preparation is key to a smooth treatment journey and optimal recovery.
DOs
- Ask Thorough Questions: Discuss treatment duration, side effects, and the impact on daily life with your doctor.
- Complete Pre-Operative Tests: Ensure all required tests (ultrasound, biopsy, scans, and blood work) are completed.
- Plan Logistics: For a smooth recovery, arrange any necessary RAI isolation or home support after surgery in advance.
- Follow Guidelines Strictly: Adhere to low-iodine diets, fasting rules, and wear comfortable clothing.
- Commit to Follow-up: Recognize the importance of lifelong hormone treatment, regular blood tests, and periodic imaging to maintain ongoing health and well-being.
DON’Ts
- Ignore Symptoms: Seek prompt medical attention for new lumps, voice changes, swallowing issues, or chronic neck pain.
- Self-Adjust Medications: Never change levothyroxine dosage or any other medication without your endocrinologist’s guidance.
- Rush Recovery: Allow ample time for healing before resuming complete or strenuous activities.
- Skip Follow-Up: Consistent monitoring (hormone treatment, blood tests, scans) is crucial for detecting potential recurrence.
- Expect a “Quick Fix”: Understand that thyroid cancer treatment is a journey requiring patience and adherence to your medical plan.
Final Thoughts
People with thyroid cancer can get complete and individualized care in Singapore. There are many choices, each one tailored to fit your health, lifestyle, and long-term needs. These include targeted radiation, active surveillance, advanced surgical techniques, and cutting-edge systemic therapies. Different types of insurance, such as MediShield Life, MediSave, and Integrated Shield Plans, can help with the financial aspects of healthcare.
Early diagnosis, thorough planning, open communication with your medical team, strict adherence to treatment plans, and a commitment to ongoing follow-up all significantly improve outcomes. Modern treatments offer excellent chances of survival and improved quality of life, even in the most advanced cases.
You should have a clear and helpful path as you deal with thyroid cancer. First, receive a thorough consultation, and then utilize tools in Singapore that are designed explicitly for thyroid nodules and thyroid cancer treatment options to help you make an informed decision about your next steps.
NC Tan Surgery – Dr Tan Ngian Chye
Farrer Park Medical Centre
1 Farrer Park Station Road
#14-02 Connexion Singapore 217562
https://nctansurgery.sg/
Phone: +65 6443 8802